The BCG Model – by the Boston Consulting Group

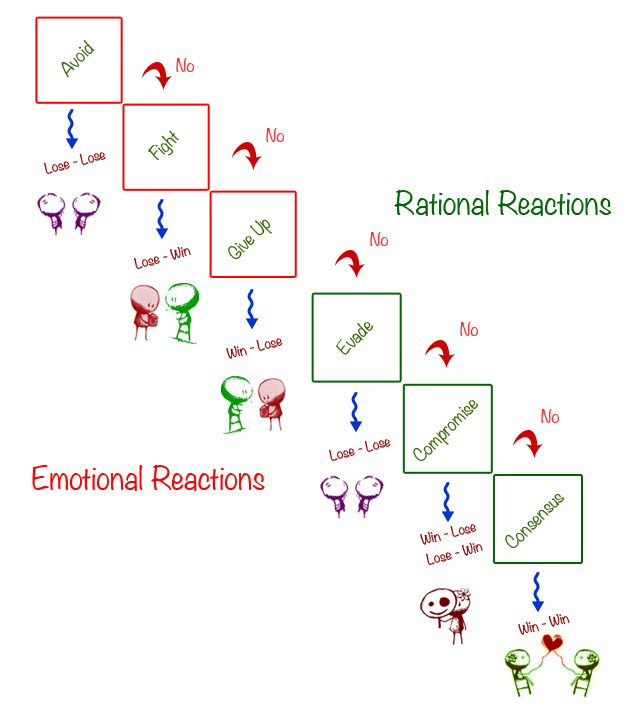
The Conflict Resolution Model
The Flow Model

Happiness, or ‘flow’ occurs when we are:
1. Intensely focused on an activity
2. Of our own choosing, that is
3. Neither under-challenging, nor over-challenging, that has
4. A clear objective, and that receives
5. Immediate feedback.
`When was the first time you did something for the first time?’
The Supermemo Model

https://www.supermemo.com/articles/theory.htm
The Swiss Cheese Model
various types of mistake:
1. real mistakes – occur when the wrong process is carried out
2. black-outs – occur when part of a process is forgotten
3. slip-ups – occur when the right process is carried out incorrectly
various levels on which mistakes occur:
1. skilled-based
2. rule-based
3. knowledge-based
various factors that contribute to mistakes:
1. people involved – boss, team, colleagues, friends
2. technical provisions – equipment, workplace
3. organisational elements – task to be fulfilled, timing
4. outside influences – time, economic climate, mood, weather
http://patientsafetyed.duhs.duke.edu/module_e/swiss_cheese.html
The Appreciation Inquiry Model – David Cooperrider and Suresh Srivastva
“…concentrating on the strengths, positive attributes and potential of a company or a person, rather than weaknesses.”
Define, Discovery, Dream, Design.
The Pareto Principal

The Chasm Diffusion Model

The Drexler-Sibbet Team Performance Model
GRPI Model
http://www.strengtheningnonprofits.org/resources/e-learning/online/leadinganonprofit/default.aspx?chp=7
Situational Leadership / Hersey-Blanchard-model

The Result Optimization Model:
“emphasis is on making things rather than planning”
